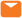
What Does Stage 4 Gum Disease Look Like?
Understanding Stage 4 Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the gums and surrounding tissues. It develops in stages, with stage 4 being the most advanced and severe. At this stage, significant damage has occurred, leading to potential tooth loss and other complications. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of stage 4 gum disease is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. In this article, we will explore what stage 4 gum disease looks like and the implications it has on oral health. What does stage 4 gum disease look like?
Signs and Symptoms of Stage 4 Gum Disease
Stage 4 gum disease is characterized by extensive damage to the gums, teeth, and supporting structures. Here are some common signs and symptoms:
1. Receding Gums:
One of the primary indicators of stage 4 gum disease is the noticeable recession of the gum line. As the disease progresses, the gums pull away from the teeth, exposing the tooth roots. This can create gaps or pockets between the teeth and gums, making it easier for bacteria to accumulate and cause further damage.
2. Loose Teeth:
As gum disease advances, the infection can spread to the supporting structures, including the periodontal ligaments and bone. This leads to the loss of bone density and weakening of the teeth. Consequently, affected teeth may become loose or shift out of position, affecting the bite and overall oral function.
3. Persistent Bad Breath:
Foul-smelling breath, also known as halitosis, is a common symptom of advanced gum disease. The bacteria responsible for the infection release toxins that contribute to the unpleasant odor. Despite regular oral hygiene practices, bad breath may persist, indicating the presence of an underlying gum disease.
4. Gum Inflammation and Bleeding:
Stage 4 gum disease is often accompanied by chronic gum inflammation and bleeding. The gums may appear red, swollen, and tender to the touch. Even minor irritations, such as brushing or flossing, can cause bleeding. In severe cases, spontaneous bleeding may occur, indicating a significant loss of gum tissue.
5. Abscesses and Pus Formation:
In advanced gum disease, the infection can lead to the formation of abscesses or pus-filled sacs. These abscesses are typically painful and may cause swelling in the affected area. If left untreated, they can lead to further damage to the surrounding tissues and contribute to the progression of the disease. What does stage 4 gum disease look like?
6. Changes in Bite and Tooth Alignment:
As the supporting bone weakens and teeth become loose, changes in bite alignment may occur. Over time, this can lead to difficulties in chewing, discomfort while eating, and a noticeable shift in the alignment of the teeth. These changes can significantly impact overall oral function and aesthetic appearance.
The Importance of Seeking Treatment
Stage 4 gum disease is a severe condition that requires immediate professional intervention. Without timely treatment, the damage caused by the disease can be irreversible, leading to tooth loss and further complications. Seeking treatment from a qualified dentist or periodontist is crucial to halt the progression of the disease and preserve oral health.
Treatment for stage 4 gum disease may involve a combination of non-surgical and surgical procedures, depending on the extent of the damage. Common interventions include deep cleaning procedures such as scaling and root planing, as well as gum surgery, bone grafting, and tooth extraction if necessary. The goal of treatment is to eliminate infection, promote gum and tissue healing, and restore oral function and aesthetics.
Additionally, implementing good oral hygiene practices at home is essential for managing stage 4 gum disease and preventing further complications. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, using antimicrobial mouthwash, and flossing daily to remove plaque and bacteria from between the teeth and along the gum line.

Regular visits to the dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups are crucial for monitoring the progress of the disease and adjusting treatment as needed. Your dentist may also provide guidance on oral care techniques and recommend specific products that can aid in managing gum disease.
It’s important to note that stage 4 gum disease is often preventable with proper oral hygiene and regular dental care. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and avoiding tobacco products, can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease or its progression to an advanced stage. For kick ass dental gum disease prevention see here.
In conclusion, stage 4 gum disease is a severe condition characterized by significant damage to the gums, teeth, and supporting structures. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of stage 4 gum disease, such as receding gums, loose teeth, persistent bad breath, gum inflammation and bleeding, abscesses, and changes in bite and tooth alignment, is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Seeking professional dental care and implementing good oral hygiene practices are essential for managing the disease, preventing further complications, and preserving oral health. Remember, prevention and early detection are key to maintaining a healthy smile.