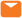
What Causes Tooth Nerve to Go Bad? Understanding Dental Nerve Damage
Introduction
When it comes to dental health, one of the most common issues people face is tooth nerve damage. Dental nerve damage can be quite painful and can lead to various oral health problems if left untreated. Understanding the causes of tooth nerve damage is crucial for prevention and timely intervention. In this article, we will explore the factors that can contribute to a bad tooth nerve, allowing you to take proactive measures to maintain optimal oral health.
1. Dental Decay and Cavities
Dental decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is a leading cause of tooth nerve damage. Cavities occur when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that gradually erode the tooth’s outer layer (enamel) and reach the inner layer (dentin). If left untreated, the decay can progress to the dental pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels, resulting in tooth nerve damage.
2. Trauma or Injury
Physical trauma or injury to a tooth can lead to nerve damage. Accidents, falls, or sports-related injuries can cause cracks, fractures, or dislodgement of teeth. When the trauma affects the tooth’s inner structure, including the nerves, it can result in tooth sensitivity, pain, or even complete nerve death. Prompt dental attention is crucial in such cases to prevent further complications. For a dental clinic croydon park see more.
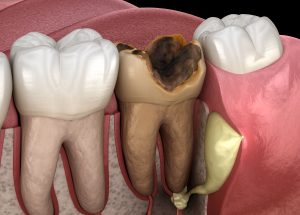
3. Gum Disease and Infections
Gum disease, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, can contribute to tooth nerve damage. Inflammation and infection of the gums can spread to the surrounding tissues, including the tooth roots. As the infection progresses, it can reach the dental pulp and cause nerve inflammation or infection, leading to a bad tooth nerve. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are essential to prevent gum disease and its potential impact on dental nerves.
4. Dental Procedures and Treatments
While dental procedures are intended to improve oral health, they can occasionally result in nerve damage. Procedures such as root canal treatments, tooth extractions, or dental implants carry a slight risk of damaging nearby nerves. Although such instances are relatively rare, they can cause temporary or permanent nerve impairment. It is crucial to choose an experienced and qualified dentist to minimize the risk of nerve damage during dental procedures.
5. Bruxism or Teeth Grinding
Bruxism, a condition characterized by teeth grinding or clenching, can exert excessive force on the teeth and their nerves. Over time, this habit can wear down the tooth enamel and expose the underlying nerves, leading to sensitivity and nerve damage. Bruxism can be caused by stress, misaligned teeth, or sleep disorders. Wearing a custom-made mouthguard, practicing stress management techniques, or seeking orthodontic treatment can help alleviate the effects of bruxism and protect dental nerves.
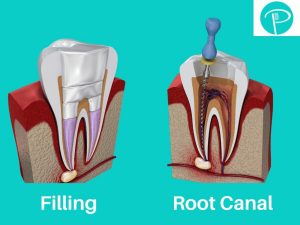
6. Dental Abscesses
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus that forms due to a bacterial infection in the tooth or gums. The infection can spread to the tooth nerve, causing severe pain and inflammation. If left untreated, the abscess can lead to nerve damage or even tooth loss. Prompt dental treatment, including antibiotics and drainage of the abscess, is essential to prevent further complications and preserve dental health.
Conclusion
A bad tooth nerve can cause significant discomfort and impact your overall oral health. Dental decay, trauma, gum disease, dental procedures, bruxism, and dental abscesses are common factors that contribute to tooth nerve damage. Taking proactive steps such as maintaining good oral hygiene, attending regular dental check-ups, using mouthguards, and seeking prompt treatment for dental issues can help prevent or minimize the risk of tooth nerve damage. Remember, early detection and timely intervention are key to preserving your dental health and ensuring a pain-free smile.
By understanding the causes of tooth nerve damage, you can make informed decisions and adopt preventive measures to keep your dental nerves healthy and functional. If you experience tooth pain, sensitivity, or suspect nerve damage, it is essential to consult a dental professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.