How to Regrow Receding Gums: Fact vs. Myth
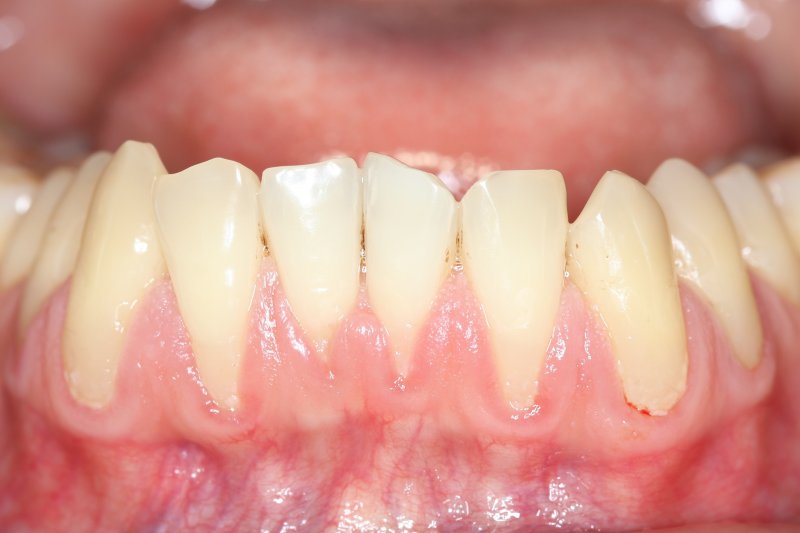
Receding gums, medically known as gingival recession, is a common dental concern that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing tooth roots and increasing the risk of sensitivity, decay, and even tooth loss. With so much information circulating online, it’s easy to get confused about what actually works. In this article, we separate fact from myth and provide evidence-based strategies for managing and improving gum health.
Understanding Gum Recession
Before exploring treatment options, it’s important to understand the causes and consequences of receding gums.

What Causes Gums to Recede?
Gum Disease: Gingivitis and periodontitis weaken gum tissue, leading to recession.
Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can damage gums.
Genetics: Some people are naturally more prone to gum recession.
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can make gums more sensitive.
Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco reduces blood flow, slowing tissue repair.
Misaligned Teeth or Teeth Grinding: These conditions put excessive pressure on gums, causing them to recede.
Why Gum Recession Matters
Receding gums are not just a cosmetic issue. They can:
Increase tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods
Expose tooth roots, making teeth more vulnerable to decay
Lead to gum disease and bone loss if untreated
Affect overall oral aesthetics and confidence
Common Myths About Regrowing Gums
There are many misconceptions about treating gum recession, and it’s important to separate fact from fiction.
Myth 1: You Can Naturally Regrow Gums at Home
Many online sources claim that gum tissue can regrow naturally with home remedies such as oil pulling, herbal rinses, or vitamin supplements. While these practices may improve oral health and reduce inflammation, there is no scientific evidence that they can regrow lost gum tissue once it has receded.
Myth 2: Gum Grafts Are Cosmetic Only
Some believe that gum graft surgery is purely for aesthetic purposes. In reality, grafting restores gum protection, reduces sensitivity, and prevents further recession, providing both functional and cosmetic benefits.
Myth 3: Brushing Harder Helps Strengthen Gums
Aggressive brushing can actually worsen gum recession. Proper oral hygiene involves gentle brushing and flossing to remove plaque without damaging gum tissue.
Evidence-Based Strategies for Treating Receding Gums
While fully regrowing lost gum tissue naturally is not currently possible, dental professionals recommend several strategies to manage and improve gum health.
1. Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
Preventing further recession starts with good oral care:
Brush twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush
Use gentle, circular motions to clean teeth and gums
Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth
Consider antimicrobial mouthwashes to reduce harmful bacteria
2. Professional Treatments
Dental interventions can restore gum health and protect exposed roots:
Scaling and Root Planing: Deep cleaning removes plaque and tartar below the gum line, reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
Gum Grafting: Tissue from another area of the mouth or donor tissue is grafted to cover exposed roots.
Pinhole Surgical Technique: A minimally invasive procedure that repositions existing gum tissue to cover roots without traditional grafts.
3. Nutritional Support
A diet rich in nutrients supports gum tissue health and reduces inflammation:
Vitamin C: Essential for collagen production and gum repair
Vitamin D: Supports immune function and bone health
Calcium: Strengthens teeth and the jawbone
Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Omega-3 fatty acids from fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts can reduce gum inflammation
4. Lifestyle Changes
Quit smoking and avoid tobacco products to improve circulation and healing
Reduce stress, which can weaken immune response
Wear a night guard if you grind your teeth to prevent further gum damage
Can Gums Fully Regrow?
The reality is that once gum tissue has receded significantly, it cannot naturally regrow on its own. However, early-stage recession can sometimes be stabilized and minor improvements in gum health can occur with meticulous oral care, proper nutrition, and professional intervention. Gum grafts and other surgical treatments are currently the most effective ways to restore lost tissue.
Preventing Further Gum Recession
Even if regrowth is limited, preventing progression is crucial:
Regular dental checkups every 6 months
Gentle, consistent brushing and flossing
Treating gum disease promptly
Avoiding habits that stress the gums, such as aggressive brushing or grinding
Summary: Fact vs. Myth
Claim Fact or Myth Explanation
Home remedies can regrow gums Myth Natural remedies may improve gum health but cannot restore lost tissue
Gum grafting is cosmetic only Myth Grafting protects roots, reduces sensitivity, and restores function
Brushing harder strengthens gums Myth Aggressive brushing damages gums and accelerates recession
Early intervention can stabilize gums Fact Good hygiene, professional care, and lifestyle changes prevent further damage
Conclusion
Receding gums are a serious dental concern that requires attention. While myths about natural regrowth are widespread, evidence-based approaches—such as proper oral hygiene, professional treatments, and lifestyle adjustments—offer the best outcomes. Early detection, combined with expert care, can prevent further gum recession, protect teeth, and improve oral health. Understanding the facts versus myths ensures you make informed decisions and maintain a healthy, confident smile.